B asic
📦 Package Managercargo
composer sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composernpm npm install some_garbage pip -
🔍📦 Search Packagescrate.io packagist.org npmjs pypi
📄 Package Configure FileCargo.toml
composer.json
package.json
-
Create Configure File
cargo new myRust或
Automatic generate when install package
npm init (-y)# 创建虚拟环境 uv venvpython3 -m venv venv#激活虚拟环境 source venv/bin/activate# 取消激活 deactivate # 生成配置文件 uv pip freeze --all > requirements.txt--all表示所有依赖(包含dev依赖) pip freeze > requirements.txt
🔩 Install Package By Configure filecargo build会下载所有依赖并编译
php composer.phar install sudo composer install npm install | npm i uv pip install -r requirements.txtpip install -r requirements.txt
🔩 Install Packagecargo add geoip2
php composer.phar require geoip2/geoip2:~2.0composer require geoip2/geoip2npm i vuenpm i -g typescript typescript 强调type,类型检查 -g: Global npm uninstall vuenpm update vuenpm view vuenpm view vue versions(linux)sudo pip install pymysqlpython -m pip install pymysqlpip install geoip2uv pip install "fastapi[standard]"
Print Version
rustc --version
composer -Vnode -vnpm -vpython3 -V
Upgrade Package Manager
rustup self update
composer self-updatenpm install npm -g(linux)sudo pip install -U pippython -m pip install -U pip
块分隔符
{ }
{ }
{ }
用缩进
if关闭fi do关闭done
语句分隔符
;
;
newline 或 ;
newline
newline 或 ;
单行注释
// comment
// comment
// comment
# comment
# comment
多行注释
/* comment line
/* comment line
/* comment line
"""
-
资源(组件/模块)引用
use include|include_once|require|require_once 复制 到使用 include 语句的文件中(代码拼接,没独立作用域)spl_autoload_register require_once 了
<script type="text/javascript" src="1.js"></script >模块化开发Demo script type="module" src="m.js"></script > 浏览器对于带有 type="module" 的 script,都是异步加载 script type="module">import { a, funca } from "./mymodule.js"funca ();script > A web-page opened via the file:// protocol cannot use import / export.
import math # math.py脚本 from math import pi,ceil #可以只导入pi或某些函数 #3.141592653589793 ceil (2.4) #3 source other.sh
Namespace组织代码和避免命名冲突的技术,php是文件拼接
没有PHP那种命名空间,使用模块系统:mod定义模块 pub表示公开可被外部使用 use引入模块路径// my_module.rs pub fn my_fun() {// main.rs mod my_module;
namespace申明必须是文件中第一个非注释语句 namespace GeoIp2\Database;class Reader implements ProviderInterface {}function Myfun() {}const MY_CONSTANT = 12;use GeoIp2\Database\Reader;use function GeoIp2\Database\Myfun;use const GeoIp2\Database\MY_CONSTANT;new Reader('xx');echo MY_CONSTANT;include ("exampleA.php");include ("exampleB.php");use function Name\exampleA\MyFun;use function Name\exampleB\MyFun; as MyFunB;// 不允许同名,使用别名
没有命名空间概念,可使用模块化 的方式来实现类似的效果。每个模块都是一个独立的作用域moduleA.js export const B = 2export function myFun() {}import { B, myFun } from 'moduleA.js'moduleB.js export default { myFun, B }import moduleB from './moduleB.js'myFun ()
没有命名空间概念,Module实现命名空间效果# moduleA.py def myFun():# main.py import moduleAprint (moduleA.B)myFun ()
-
装饰器或宏
Macros
#[Attribute] PHP8
TypeScript
@decorator
-
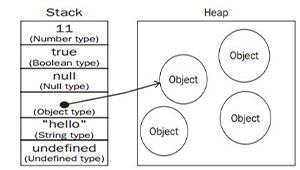
V alue & Type
命名
区分大小写,可使用中文命名,使用蛇形命名法
变量常量名区分大小写,函数class名不区分,变量需$开头,可使用中文命名,比如 $数量=300
区分大小写,可使用中文命名
区分大小写,可使用中文命名,使用蛇形命名法
区分大小写,不可使用中文命名
基础数据类型
栈上存储:数据类型大小已知,小而固定,是Copy类型。整型[栈|Copy] const HEX_NUM: u8 = 0xff; //二进制 浮点型[栈|Copy] let y: f32 = 1.0;Boolean[栈1字节|Copy] let f: bool = false ;Char字符类型[栈4字节|Copy] let z: char = '😊';Tuple元组型[栈|Copy] let tup: (i32, f32, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);&str[栈指针8+长度8字节,指向堆上数据|Copy] let str: &str = "abc"; // 要用双引号 String[堆|非Copy] let mut str = String::from ("abc");数组型vec(T)[堆] let a: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
整型 浮点型 string Boolean FALSE ;null NULL ;Object new foo ;number型 var x = 0; // typeof(x)的值是"number" BigInt型 String (BigInt (1)+BigInt (Math.pow (2,53)))string型 var str = "";boolean型 var b=false;undefined型 var a = undefined object型 var car = null ; // typeof(car)的值是"object",null值是一个空的对象指针 var obj = {}; // 同= new Object();typeof值object var arr = []; // 同= new Array(); typeof值object var re=/regexp/g; // typeof值Object 同= new RegExp("regexp","模式修饰符g全局模式应用所有字符串,i区分大小写,m多行匹配") var foo = function () {} // typeof值function 引用(reference)值 分配给变量时,空间需要在堆(heap)上分配, 引用值不能像原始(primitive)值 直接分配在栈(stack)上,因为它没有固定的尺寸,所以它将内存地址存在栈上, 作为一个指针TypeScript // 数组 // 数组另一种表达 // 元组 number型 string型 Boolean型 # True/False 空型 Object型 Car ('Ferrari',570)bash中的所有变量都是string ,无论有没有加引号echo $PWD
类型安全
fn greet(name: &str) -> String {
function greet(string $name, int $age): string {
TypeScript
def get_name_with_age(name: str, age: int) -> str:
-
内存回收♻️
Rust在编译时通过所有权,借用和切片来确保内存安全,数据超出作用域会自动被清理。let a = String::from("Hello");let b = a; // a 把所有权转移给b println! ("{}", a); // 编译错误!a已经死了 let hello = &s[0..5];
自动回收
自动回收以前引用计数(无法解决循环引用) 现标记清除+碎片🧩 整理
自动回收
数据类型判断
-
echo gettype ("mark"); // string typeof value==="undefined"var theHobbit = new Book ('07122-4', 'The Hobbit', 'J. R. R. Tolkein');instanceof Book; //值为true, 某类的实例 print (type (value))print (isinstance (12, int)) # True print (isinstance ('hi', str))print (isinstance ([1,2], list))都是string
🌍 作用域let x = 5;let x = x + 1;let x = x * 2;println !("在块级作用域中x的值是: {x}"); // 12 println !("x的值是: {x}"); // 6 1. PHP是文件拼接 文件之间不是独立作用域 ,不像python/node的import和rust use是非代码拼接,作用域隔离(要export变量)函数内不能读函数外的非全局变量 global 关键字可实现在函数内使用外部变量(Rust|Python|JS不需要)function b() {global $a;echo $a;3. 无块级作用域 $GLOBALS 1. 无var 申明, 都是全局的global/globalThis (Node.js)// 值为hello this .myglobal; // 值为hello // 值为hello var 局部变量,函数内可以沿着作用域链 调用外层变量let, const 设置的变量/常量可限制在块级作用域 内使用while (){} | if (){} | try {} catch (e){}| for (let i=0;i<10;i++){ 每一个循环都是一个作用域 }var a = []for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {function () { console.log (i); };// output: 6 如果上面i前的let 改成var 他的结果就是10
值变参分割变量作用域 for (var i = 0; i < 10; i++) {function (i) {function () { console.log (i); }执行上下文
local (默认): 局部变量nonlocal : 非局部变量,用于闭包global : 全局变量没有作用域,函数内外可互相访问function display(){echo $a# 好 echo $b # 玩
闭包(closure) 闭包就是能够读取其他函数内部变量的函数 有
使用 use 关键词function counter ()return function () use (&$i) {return ++$i."\n";counter()echo $nays()echo $nays()
var counter = function () {var i=0;return function () {return ++i;var nays = counter(); log (nays()); // output: 1 log (nays()); // output: 2 def counter ():def foo ():nonlocal i # 申明非局部变量 return ireturn foo counter ()print (nays ()) # output: 1 print (nays ()) # output: 2 判断变量是否存在
if (!empty ($v)){}//null 或未定义或''或0 或FALSE 为TRUE if (is_null ($v)){}//null 或未定义为TRUE if (isset ($v)) {}// 非null或已定义为TRUE if (typeof (var_name)=='undefined') { //不存在 }a='mark'print ('a' in globals ()) # True print ('a' in locals ()) # True print ('b' in globals ()) # False
if [ ! -n "$1" ]; then # 变量是否存在 获取资源类型
get_resource_type() -
- -
变量的变量
$a='hello';echo ${$a}; //等同于echo $hello; - - -
const常量是在程序运行时不会被修改的量
Rust默认变量是不可变的,必须加上mut,而const是编译时就能确定的变量,但有些值在运行时才有 const user_input = std::io::stdin ().read_line ().unwrap (); // 编译错误 let mut x = 5;或 let x = 5;let x = 6; x变量被第二个shadowed let spaces = "***";let spaces = spaces.len (); // 3 let mut spaces = "***";len (); // 错误:expected `&str`, found `usize`
define定义的常量可跨脚本跨函数-全局常量define ("PI", 3.14); // define()在函数里定义的常量在外面依然可使用 const PI='3.1416'; //const定义的必须处于最顶端的作用区域
const PI = 3.1416; // TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. const foo;// Uncaught SyntaxError: Missing initializer in const declaration if (true ) { const MAX = 5; }log (MAX) // Uncaught ReferenceError: MAX is not defined const的作用域与let相同,只在声明所在的块级作用域内有效 const a = {}; a.a = 1; 对象的属性能改变,const只能保证这个指针是固定的 没有常量
-
enum通常用来表示如color, type, status等数目有限、形式离散、表达明确的量
enum Level {PHP8.1引入
TypeScript支持enum LogLevel { ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, }
enum模块
-
set value
let a = 1; 无链式赋值let y = {let x = 3;// 4 $v = 1;$a=$b=3; var v = 1;var a=b=3建议使用下面的single var模式 a=1;b=c=3 myname=mark 注意等号=两边不能有空格,不然会被当成命令,如果值中间有空格就要加引号如"mark li" echo 后面的字符中有空格可以不加引号
并行set value
let (x, y, z) = (1, 2, 3); // 元组解构 list ($y,$z)=array (2,3); //把数组中的值赋给一些变量 var x=1,y=2,z=3字符串解构赋值 let [a, b, , c, d] = 'abcde'; // d == 'e' 数组解构赋值 let [, b, c] = [1, 2, 3]; // c == 3 Set数据解构赋值 let [a,,c]=new Set ([1,2,3]); // c == 3 对象解构赋值 let {x,y} = {z:2,y:3,x:4} // x == 4 y == 3 属性的解构赋值 let {length : len} = 'hello'; // len == 5 let [head, ...tail] = [1, 2, 3, 4];// tail=>[2,3,4] 解构赋值 -
🤹♀️ swap(a, b) = (b, a)
list ($x, $y) = array ($y, $x);[a,b]=[b,a];
a, b = b, a
-
Proxy 拦截
-
?
拦截对象 getter setter defineProperties (flashvim, {log ('拦截读值')return cmdlog ('拦截设值') // 拦截设值 单个属性 defineProperty (flashvim, "cmd", { configurable: true... // Object.defineProperty 官方建议弃用 拦截对象 getter setter new Proxy ({}, {log ('拦截取',key, '的值')return target[key]log ('拦截设', key, '的值', newval)return target[key] = newval // 拦截设 cmd 的值 拦截数组 getter setter new Proxy (arr, {log ('拦截取',key, '的值')return target[key]log ('拦截设', key, '的值', newval)return target[key] = newval // 拦截设 cmd 的值 ?
-
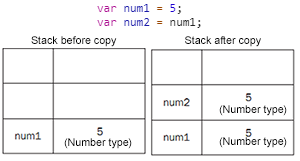
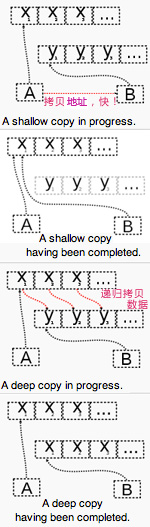
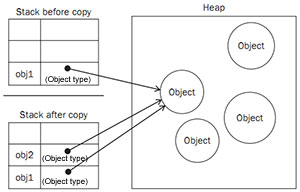
copy -
默认深拷贝
原始值拷贝的是数据 数组/对象默认浅拷贝
-
数组/对象copy
-
$a = array (1,2,array (3,4));& $a; //浅拷贝 //深拷贝
引用值拷贝的是指针地址,所以两个对象指向相同的堆 var a = [1,2,[3,4]];var a2=a; //浅拷贝 var a3=JSON.parse (JSON.stringify (a)) //深拷贝 a = [1,2,[3,4]]#地址拷贝 copy ()#深拷贝
-
🧊 Freezes an object-
-
var day = ['Mon','Thu','Wed', 'Thu', 'Fri', 'Sat', 'Sun'];var d = day;Object .freeze (day);// output: Mon // output: Mon frozenset ()-
charCode 字符编码let c2i = 'a' as u32;let i2c = char::from_u32 (97).unwrap ();String .fromCharCode (97) // 'a' charCodeAt () // 65 N umber and Operators逻辑运算符
┏━━⁄ ━━━━🔋━┓ and
┗━━⁄ ━💡━━━━┛
┏━⁄ ━┓ or
┣━⁄ ━┻━━━🔋━┓
┗━━💡━━━━━━━┛
电阻
┏━⁄ ━━⬇━━━━┓ not
┣━━━━━▭━━🔋━┫
┗━━💡━━━━━━━┛
&& || !
&& || !
&& || ! false ) === 0false && 0) === false true || 3) === true false || 3) === 3算术运算符 +-*/ 比较运算符 === 的优先级高于逻辑运算符所以带括号 ⚠️ &&优先级高于||
and or not
if [ $env != "dev" ] && [ $env != "test" ];then exit fi % echo 1 && echo 2% echo 1 || echo 2% echoo 1 || echo 2% echoo 1 && echo 2位运算符
按位与 按位或 按位异或 按位取反
101 101 101
&1100 |1100 ^1100 ~0101
━━━━━ ━━━━━ ━━━━━ ━━━━━
0100 1101 1001 1010
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 -2<<1
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111100 零填充左位移 -4
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 -2>>1
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
1 1111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 有符号右位移
填充符号位(32位最左侧的一位,正数为0 负数为1)
11111111 11111111 11111111 11111110 -2>>>1
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
0 1111111 11111111 11111111 11111111 零填充右位移 -1
a&b a|b a^b !a a<<b a>>b
a&b a|b a^b ~a a<<b a>>b
a&b a|b a^b ~a a<<b a>>b a>>>bvar CHUNK_SIZE = 5 << 20 // 5M,FF=256=8个0,1K=1024=10个0 if (~'markbuild'.indexOf ('mark')) {}
a&b a|b a^b ~a a<<b a>>b
比较运算符等于,不等于,大于,小于,不小于,不大于
== != > < >= <=
== != > < >= <=<>也可以表示不等于
== != > < >= <====全等(值和类型)
== != > < >= <=
对于数字 -eq -ne -gt -lt -ge -le
算术运算符加,减,乘,除,余数
+ - * / %/ 没有类型转换
+ - * / %/ 整除则是整数,否则小数
+ - * / %/ 整除则是整数,否则小数
+ - * / %/ 至少保留一位小数位
echo $[m+n]/整型
整除÷
let quotient = a / b;
(int ) (13 / 5) parseInt (13/5)13//5 floor整除 divmod (除÷法的余数)
let remainder = a % b;$d=(int )(10/3); d=(parseInt )(10/3); divmod (10,3)#输出(3,1) 赋值运算符x=y,x=x+y,x=x-y,x=x*y,x=x/y,x="x""y",x=x%y
= += -= *= /= .= %= = += -= *= /= += %= 同Javascipt 递增++递减--
-
++x;
++x;
无,用+=1 $[--i]
乘方2⁴, 三次方根 ∛8
let result = 2i32.pow(4);
pow (2, 4)pow (8, 1/3)2**4 #输出16 pow (2,4)pow (8, 1/3)
2**4 #输出16 pow (2, 4)pow (8, 1/3)
开方求平方根(二次方根) √
(4.0f64).sqrt()
sqrt (4)Math.sqrt (4) import mathsqrt (4)浮点转换round四舍五入或银行家舍入法(奇进偶舍) ceil(天花板)入 floor(地板)舍
x.round()
(int )$xround ($x) // 四舍五入 ceil ($x)floor ($x)
Math.round (x) // 四舍五入 ceil (x)floor (x) parseInt (x)
int (x)round (x) // 奇进偶舍 floor (x + 0.5) // 四舍五入 round (5.5) == round (6.5) // True import mathceil (x)floor (x)保留 n 位小数
format("{:.1}",x);.1表示保留1位小数
number_format (6, 1)(6).toFixed (1) // 6.0 返回字符串,toFixed 是 Number 类型的方法
"{:.1f}".format (6)
最小值最大值
min (1, 2, 3);max (1, 2, 3);array (1, 2, 3);min ($a);max ($a);Math.min (1,2,3);max (1,2,3);min (...arr) // ES6
min (1, 2, 3);max (1, 2, 3);min (arr);max (arr);绝对值
x.abs()
abs ($x)Math.abs (x) abs (x)-
随机数 🎲
⚀⚁⚂⚃⚄⚅
[dependencies]
rand (0,99)Math.random () 0.0 ~ 1.0 之间的一个伪随机数 import randomrandom ()echo $((RANDOM % 100 +1))echo $(jot -r 1 1 100) # jot 还可以生成随机字符串进制转换十进制与10根手指👐 有关
bindec ('101')hecdec ('aa')decbin (5)dechex (170)dec to hex/bin Number (n).toString (16)Number (n).toString (2)hex/bin to dec Number (0xaa)Number ('0xaa')Number ('0b101')Number (0b101)int ('101', 2)int ('aa', 16)bin (5)hex (170)-
S tring字符串数据
┏━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━┳━━┓
┃d┃o┃n┃'┃t┃ ┃s┃a┃y┃ ┃"┃n┃o┃"┃\0┃
┗━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━┻━━┛
$str = "don't say \"no\"";echo 'don\'t say "no"';
str = "don't say \"no\"";log ('don\'t say "no"')
s = "don't say \"no\""print ('don\'t say "no"')
echo "hi,$var\!"变量不能用于单引号中,!用不能直接用在双引号中
变量in字符串
-
$count = 3;echo "$count ${item}s\n";
const count=3const item = "ball"或 str = String.raw `$(count) ${item}s`// 函数in 字符串,`` 字符串支持换行 -
echo "hi,$var\!"
格式化输出
echo sprintf ("lorem %s %d %f","ipsum", 13, 3.7);-
print ('Hi, %s, you have $%d.' % ('Mark', 1000000))printf "%-5s %-10s %-4.2f\n" 3 Mark 61.563
📐 lengthstrlen ("lorem")str.length len (str) echo ${#varname}
get字符串中第n个☝ 字符
$s[6]
s[6]charAt (6)
s[6]# 倒数第一个字符 # 输出ipsu 还有s[6:]和s[:-1}
echo ${a:5:1} # 第6个字符
set字符串中第n个☝ 字符
$s = "bar";echo $s; //输出baz
s.slice(0, index) + 'z' + s.slice(index+1) // JS 中字符串是不可变的(immutable)数据类型,一旦创建了一个字符串,就不能修改它的内容
Python 中的字符串是不可变对象,你不能直接修改字符串的某个字符。可以通过创建一个新的字符串来达到修改字符串的效果 -
字符串遍历
for ($i = 0; $i < strlen ($str); $i++) {echo $str[$i];for (let char of 'foo') {for char in "mark":print (char)-
字符串是否包含/在字符串中的位置
if(strpos ('mark li', " ")===false)右边字符串在左边字符串中首次出现的位置,没有返回false 注意有可能在第一个位置返回0
var st = "do re re"; if (st.indexOf ("re") >= 0 )// lastIndexOf()从未尾开始查找 includes ("ar") // output: true startsWith ("https://markbuild.com")endsWith ('markbuild.com')用正则的 re.findall (r're',st)in 'mark'endswith ('build')startswith ('mark')echo "$str" | grep -q "$substr"if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "包含子字符串"else echo "不包含子字符串"fi 合并字符串
$s2 = $s ."World!";
s += 'World!'concat ('World')
'hello' + 'world' c=$a$b
repeat
str_repeat ('+---', 3)'+---'.repeat (3).concat ('+')// +---+---+---+ 3 * '+---' + '+'
-
✂ 字符串定位切割子字符串substr ("lorem ipsum", 6, 5)第6+1个字符串起,往后切5个 str.slice (6,11)保留str[6]~str[11-1] substr (6,5)官方不建议使用
s[6:11]
str=mark.echo ${str: -1} # 获得最后一个字符 显示. ⚠️注意空格 echo ${str: :-1} # 去掉最后一个字符 显示mark ⚠️注意空格 echo ${str:0:4} # 显示mark echo ${str:4} # 显示.
全部大小写
strtoupper ("lorem")strtolower ("LOREM")"lorem".toUpperCase ()toLowerCase () s.upper ()lower ()
-
字符串首,单词首大写
ucfirst ("lorem")ucwords ("lorem ipsum")-
s.capitalize ()title ()
-
去掉两边的空格(默认),或其它字符(非串)
trim (" lorem ")ltrim ("/category/page/5","/")rtrim ("12,4,6,",",") 同 chop ("12,4,6,",",")" lorem ".trim() trimLeft () .trimStart ()trimRight () .trimEnd ()
" lorem ".strip()
-
Reverse 🔁
echo strrev('mark');// kram str.split ('').reverse ().join ('')
print (str[::-1])echo "mark"| rev # kram 数字转字符串
"value: ". 8 String (num)toString ()str (4)-
字符串转数字
7 + "12" Number ("73.9")int ('4')-
[Array ] 数组转字符串
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓
┃ do┃ re┃ mi┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
┏━━━━━━━━━━┓ ↵
┃ do,re,mi ┃
┗━━━━━━━━━━┛
$arr = array ("do",re","mi","fa");implode (",", $arr) ["do", "re", "mi", "fa"].join (",");toString (); // Output: "do,re,mi,fa" lista=["do","re","mi","fa"]join (lista)join (str (i) for i in b) [Array ] 字符串转数组
┏━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ do,re,mi ┃
┗━━━━━━━━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ do┃ re┃ mi┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
explode (",","do,re,mi,fa")\n是指换行符 var arr = "do,re,mi,fa".split (',');// str.split(',',3) 只保留前3段 split (/\s+/) // 支持正则字符 s="do,re,mi,fa"split (',')list ('123')for i in range (len (s))]split ()和js不一样,py不支持.split ('')为空字符串,要用上面的list (str)
-
[Array ] 字符串中每一个字符分割到数组
┏━━━━━━┓
┃ abcd ┃
┗━━━━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ a ┃ b ┃ c ┃ d ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
str_split ("abcd")str.split (''); l=list (s)
-
非正则替换
echo str_replace ('world', "sun", "hello world");'hello world world'.replace ('world', 'sun') // hello sun world replaceAll ('world', 'sun')// hello sun sun
"hello world world".replace ("world", "sun") # hello sun sun
-
eval
?
?
eval ('alert("mb")')eval ('print("mb")')?
统计子串出现的次数
?
?
str.split (substr).length - 1
len (str.split (substr)) - 1?
R egular Express 🧩
正则替换
$s = "do re mi mi mi";preg_replace ('/mi/', "ma", $s);
var s="do re mi mi mi";var s2=s.replace (/mi/g,"ma");replace (/([^<]+)<\/font>/g,"$1");replace (/\.([^.]+$)/,function ($0) { return '_360x'+$0 }) s="do re mi mi mi"sub (r'mi',r'ma',s)
sed '1,2s/mark/mk/' file # 替换1,2 行的第一个mark sed '1,2s/mark/mk/g' file # 替换1,2行每行上的所有mark sed -in-place 's/mark/mk/g' file # 替换所有行上的所有mark, 并保存到原文件 匹配
if (preg_match ('/1999/', $s)) {echo "party!\n";if (s.match (/1999/)) {log ("party!");search (/>M/i) //2 ,如果没有匹配则返回-1 exec ("mark li") // [" li", index: 4, input: "mark li"], 不匹配则返回null 全局匹配,⚠️ 如果非//g 的正则会死循环 while (res = reg.exec (data)) { console.log (res[0]) } // 全局匹配,直到res 为 null split (/\s+/); // ["2", "3", "4", "5"] import relen (re.findall (r'1999',s2))>0[[ "$1" =~ ^[0-9]{0,2}$ ]] && echo "yes"
捕获
$regex = '/^type=(9)&code=([0-9]{6})$/';array ();if (preg_match ($regex, $str, $matches)){echo 'type='.$matches[1];echo 'code='.$matches[2];
/page=([0-9]+)/.exec ('&page=52&')[1] // 52test ('&page=52&')){alert (RegExp .$1*1+1);} // 53
match = re.compile (r'\d+').search ('123mark456')
动态构造正则
new RegExp (str+'$')A rray/Set定义/申明
$arr = array (1, 2, 3, 4);
var arr=[1, 2, 3, 4];new Array(10).fill ().map ((itm, idx) => idx)from ({ length: 10 }).map ((itm, idx) => idx)var set1=new Set()var set2=new Set([1,2,3])WeakSet 的成员只能是对象且不能forEach,并且和WeakMap一样是弱引用,如果存储的对象被GC, 它在WeakSet 里自动释放 前端常见内存泄漏及解决方法 TypedArray 比Array省内存,长度是固定的,开了空间就不能改,他的值他存的是实际数据而不是指针Int8Array 存-128~127范围的数字,超出范围取模后余数Uint8ClampedArray 和 Uint8Array 都是用来存0~255的数字,Unit8Array超出范围取模余数, 对于260和-10转化为4和246,Clamped对于260和-1转化为255和0,适合图像颜色计算Uint16Array 存0~65535范围ArrayBuffer TypedArray 和 DataView l=[1, 4] # list # tuple 不可修改元素值,元素个数 # set 无序不重复 # nest
arr=(1 2 3 4 5)
📐 length/sizecount ($arr)count ($d)arr.length
len (squares)echo ${#arr[*]}Get value by index☝
$arr[0]
arr[0]at (-1)// 先转化成数组
squares[0]
echo ${arr[0]}Set value by index☝
$arr[0] = "lorem";
arr[0]="lorem";add (1)
squares[0]="lorem"
arr[0]="hi"
Fill 填充
['vscode', 'notepad++', 'xmind', 'postman'].fill ('terminal')
value是否存在 于arrayindex of array elementcount 在array中出现的次数
if (in_array (2, $a)){}array_search ("y", $arr);['mark','emy'].indexOf ('mark')>=0; includes ('mark') // ES5+ has (3)
'm' in ['a', 'b', 'c'] # True/False try :index ("y")print ("y第1次出现的位置", idx)except ValueError:print ("not in list")count ('m') > 0: # 返回2 统计出现的次数
✂ 数组slice切片选择第3,4个元素
┏━┳━┓✂┏━┳━┓ ✂┏━┓
┗━┻━┛ ┗━┻━┛ ┗━┛
array_slice ($arr, 2, 2)arr.slice (2,4) // 切取 arr[2] ~ arr[4-1] slice (-2,-1) // 获得倒数第2个
squares[2:4] ✂ slice to end 数组切到底
┏━┓✂┏━┳━┳━┳━┓
┗━┛ ┗━┻━┻━┻━┛
array_slice ($arr, 1)arr.slice (1)
squares[1:] 数组首部操作,追加与删除元素
┏━┓ +┏━┳━┳━┳━┓
┗━┛ -┗━┻━┻━┻━┛
?
var arr = [6, 7, 8]unshift (5)shift ()?
数组尾部操作,追加与删除元素
┏━┳━┳━┳━┓ +┏━┓
┗━┻━┻━┻━┛ -┗━┛
$arr = array (6, 7, 8);array_push ($arr, 9);# 与array_push相同 array_pop ($arr);删除尾部元素
var arr = [6, 7, 8]push (9)pop () 或 arr.length--list1.append (9)pop ()
Insert an item into an array at a specific index☝
arr.splice (_index, 0, item)
删除元素by index☝
unset ($arr[_index]);//数组将不会重建索引,若要重建索引用array_values($arr) arr.splice (_index,1)//前面一个参数数是删除的index,后面一参数表示删除后面的几个元素 delete arr[_index];//仍会占据一个长度,值为undefined
del a[0]#删除2个 全部删除或 squares.clear ()删除元素by value
arr.splice(arr.indexOf('v'), 1)
合并
┏━┳━┳━┳━┓ +┏━┳━┳━┳━┓
┗━┻━┻━┻━┛ +┗━┻━┻━┻━┛
$arr = array (1, 2, 3);array (1, 2, 3);print_r (array_merge ($arr,$arr2));
var arr = [1,2,3],log (arr.concat (arr2));... 扩展(Spread)运算符 log ([...arr,...arr2])squares+[2,4,'mark']扩展数组 list1.extend (list2)
数组遍历
ↆ
┏━┳━┳━┳━┳━┓
┗━┻━┻━┻━┻━┛
foreach ($arr as $s) {echo "$s\n";foreach ($arr as $i => $s) {echo "$s at index $i";⚠️ for in 中的index 不是数字,是字符串,而forEach中的index 是数字
for (idx in ['v']) { console.log(8+idx) } // 输出80
forEach ((item, index) => {})
forEach 无法用break 跳出可以用every 或some或find
every是遇到false就终止并返回false,some是遇到true就终止并返回true,find/findIndex是遇到true就终止并返回那个满足条件的item/index
every ((item, index) => { /* 相当于break */ some ((item, index) => { // 或arr.find( /* 相当于break */ for (let item of arr) {
for v in squares:将范围转成数组
$a = range (1, 10);
-
a = list (range (1,10)) Reverse
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓
┃ M ┃ a ┃ r ┃ k ┃ 🔁
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ k ┃ r ┃ a ┃ M ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
$a = array (1, 2, 3);array_reverse ($a);print_r ($a);
var a = [1, 2, 3];reverse ();log (a);reverse ().join(' ')===a.join(' ') 一定为真,reverse 操作数组本身 l=[1,2,3]reverse ()print (l)
SortASCII code
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓
┃ M ┃ a ┃ r ┃ k ┃ 📶
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ M ┃ a ┃ k ┃ r ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
$a = array ("b","A","a","B");sort ($a);print_r ($a);
.sort原数组排 .toSorted产生新数组toSorted () // [15, 5, 6] 按字符串排序, 15会排在5前,因为起始字符是1 toSorted ((a,b)=>a-b) // 数字排序 sort compare回调返回的必须是数字,不是true 或 false,否则出错
sort ((a,b) => a<b) // ❌['ab','aa','bb']
sort ((a,b) => a<b?-1:1) // ['aa','ab','bb']
Object .keys (obj).sort ((a,b) => {if (obj[a] === obj[b]) {return a.charCodeAt () - b.charCodeAt ()else {return obj[b] - obj[a]Array .from (set).sort () // Set 没有数组方法
.sort原数组排 sorted产生新数组sorted ([15,6,5]) [5, 6, 15] 跟js不一样 sort (key =lambda x: (-x[1], x[0]))sorted (ListA, key =lambda x: x[1], reverse =True)
重复数据删除(去重)
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓
┃ M ┃ o ┃ o ┃ n ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ M ┃ o ┃ n ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
$a = array (1, 2, 2, 3);array_unique ($a);
arr = [1,2,3,3] Array .from (new Set (arr)) 或者 [...new Set (arr)]
-
洗牌和取样
⚀⚁⚂⚃⚄⚅
$a = array (1, 2, 3, 4);shuffle ($a);//洗牌 array_rand ($a, 2);//随机截取
-
-
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓
┃ ( ┃ { ┃ [ ┃ ? ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
┏━━━┳━━━┳━━━┓ ↵
┃ ( ┃ { ┃ [ ┃
┗━━━┻━━━┻━━━┛
arr.filter (item=>item>10)设置过滤后长度为0时的默认值 filter (condition).concat ({ field: 'default' })[0].field
按条件查找
[88, 93, 95].find (item=>item>90) // 93 findIndex (item=>item>90) // 1
Reducer
arr.reduce ((acc, item) => {return acc
from functools import reducereduce (lambda acc, item: acc + item, [1,2,3,4], 0)Map
collections.map ((item)=> item.title)// ['title1', 'title2', 'title3'] // 获得数组中数字为奇数项的index map ((itm, idx) => itm % 2 ? idx : -1)filter (item => item !== -1)
def myfun (x):return x * xlist (map (myfun , [2, 3]))list (map (lambda x: x * x, [2, 3]))扁平化Flat
[1,2,[3,4],[[5,6]],[[[7,8]]],[[[[9,10]]]]].flat (2) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, Array(2), Array(1)] flat (Infinity) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10] flatMap (item=>item.split (' ')) // ['May', 'the', 'force', 'be', 'with', 'you']
O bject/Map/Dict/struct定义/申明
$d = array ("t" => 1, "key" => 0);
var obj={t:1,key:0}const map1=new Map();set (b, 'v')get (b)const map2=new Map([["k1","v1"],["k2","v2"]]);map2.get ("k1") // v1 WeakMap的key 必须为引用值,当这个key不被引用,会被GC 回收,从而从WeakMap 里自动释放, WeakMap且不能被forEach。Map 的 key 啥类型都行,但影响GC 回收该key 导致内存泄漏,Map支持forEach new WeakMap()前端常见内存泄漏及解决方法 d = {"state": 4, "action": "VO"} # dict
declare -A tel
📐 length/sizemap1.size
Get value by key🔑
$d["t"]
_obj.t 或 _obj["t"]
d['jack']
echo ${tel[Mark]}Set value by key🔑
?
map2.set("k3","v3");// stars set to 4
d['jack'] = 5
tel[Mark]=6016
key🔑是否存在
if (array_key_exists ("key", $d))'key' in objhas ('key')
if 'jack' in tel:#还可以使用not in 删除元素by key🔑
unset ($d["t"]);delete _obj.t;del tel['sape']合并覆盖Object
?
Object.assign (default_opt, opt)... 扩展(Spread)运算符
对象遍历
foreach ($d as $k => $v) {echo $k.'=>'.$v;}for (let key in arr_obj){log (arr_obj[key]);for v in d:Get all keys🔑🔑 & Get all values 转成数组
array_keys ($d)array_values ($d)Object.keys (obj) // Output ['t', 'key'] values (obj) // Output [1, 0] entries (obj) // Output [['t', 1], ['key', 0]] 注意对象输出是按插入顺序而不是名称排序 keys (obj)[0] === 'B' // true
list (tel.keys ())list (tel.values ())
F unction
定义函数
fn main () {let result = myFunction ("World");println! ("{}", result);fn my_function (name: &str) -> String {format! ("Hello {}", name)function add3 ($x1, $x2, $x3)return $x1 + $x2 + $x3;function add3 (x1, x2, x3) {return x1 + x2 + x3;function add3 ([x1,x2,x3]) { return x1+x2+x3;}function myfun ({x,y,z}) { return x*y-z;}def add3 (x1,x2,x3):return x1+x2+x3function add3 (){echo $[$1+$2+$3]Arrow Function有点像pipeline,箭头前的输出是箭头后的输入
-
-
箭头函数可省去return // 等价于: => { return expression; } 只返回{}, 应当用()将其包起来, 否则当statements处理而不是当expression处理 如果只有一个参数,可以不加圆括号: 无参数的箭头函数需要使用圆括号或者下划线 箭头函数的this始终继承父级作用域的,且不能作为构造函数 -
- 调用函数
宏(!) println! ("Hello,{}", name); 的本质是:write_fmt (&mut std:io:stdout (), format_args! ("Hello, {}", name));let numbers = vec![1, 2, 3]; 的本质是:let mut numbers = Vec::new();push (1):push (2);push (3);add3 (1, 2, 3);add3 (1, 2, 3)add3 ([1,2,3]);myfun ({x:3,z:2,y:1});// output: 1 add3 (1, 2, 3)add3 2 3 8 #打印结果13 数组作参数
?
$arr = array (1, 2, 3);function foo ($ar){}echo foo ($arr);
... 扩展(Spread)运算符 log (foo (...arr))max (...arr)l=[1,2,3]def foo (arr):for v in arr:print (v)foo (l) rest参数
?
-
function add (...values) {for let v of values){add (2,5,7)函数作参数
?
function add ($x,$y,$f){return $f($x)+$f($y);function add (x,y,f ){return f (x)+f (y)def add (x, y, f ):return f (x) + f (y)默认参数
?
function my_log ($x, $base=10)return log ($x) / log ($base);my_log (42);my_log (42, M_E);function my_log (x, base)return Math.log (x) / Math.log (base);my_log (42);my_log (42, Math.E);function my_log (x, base=10)import mathdef my_log (x, base=10):return math.log (x) / math.log (base)my_log (42);my_log (42, math.e)可变数目的参数
?
function first_and_last ()func_num_args ();if ($arg_cnt >= 1) {func_get_arg (0);echo "first: " . $first . "\n";if ($arg_cnt >= 2) {func_get_args ();echo "last: " . $last . "\n";function howManyArgs (){log (arguments.length);log ("Hello"+arguments[0]+","+arguments[1]);howManyArgs ("string", 45);Python可变参数 传地址参数
?
function foo (&$x, &$y)foo ($n, $s);-
-
匿名(Anonymous)函数
?
$sqr = function ($x) {return $x * $x;echo $sqr(3);
IIFE(Immediately-Invoked Function Expression)立即调用函数表达式 function () {})()function () {}())lambda用于创建匿名函数 回调模式
?
call_user_func ('myfun')call_user_func ('myfun','myparam')function call_func (function_param) {function_param ();function myfunc () {call_func (myfunc);def callback (fun):fun ()def myfun ():callback (myfun)sync and async
//异步1: Callback getData (a => {getMoreData (a, b => {getMoreData (b, c => {//异步2: Promise function getData () {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {readFile (fileName, (error, data) => {if (error) { reject (error) }else { resolve (data) }getData ()then (a => getMoreData (a))then (b => getMoreData (b))then (c => {})catch (err => {})//异步3: async/await, async 是Generator 的语法糖 const foo = async function () {try {let a = await this .apis.getData ()let b = await this .apis.getMoreData (a)catch (err) {}
定义类
-
class Book {private $isbn; public $title; public $author; public function __construct ($isbn, $title = null, $author = null) { // 构造函数 public function display () {echo $this->isbn;var Book = /** @class */ function (isbn, title, author) {if (isbn == undefined) throw new Error('Book constructor requires an isbn.');this .isbn = isbn;this .title = title || 'No title specified';this .author = author || 'No author specified';prototype .display = function () {//或者 prototype = {checkIsbn : function (isbn) {display : function () {ES6 的类是基于原型语法的语法糖 class Book {constructor (isbn, title, author) {if (isbn == undefined) throw new Error ('Book constructor requires an isbn.');this .isbn = isbn;this .title = title || 'No title specified';this .author = author || 'No author specified';display () {log (this .isbn)get stars () {return 5set stars (newval) {class Car:def __init__ (self,brandname,horsepower):def drive (self):print ('Run with %s horsepower' % self.power)也可以这样玩 class Car:pass Using a Class to Instantiate an Object
$theHobbit = new Book ('isbn', 'The Hobbit', 'mark')
var theHobbit = new Book ('isbn', 'The Hobbit', 'mark')?
method
$theHobbit->display ();
theHobbit.display ();
Ferrari458.drive()
value
$theHobbit->isbn; // Cannot access private property Book::$isbn // 动态
theHobbit.isbn
Ferrari458.brand
访问修饰符实现封装,减少耦合
public :全开protect :仅同一个类或子类能访问private :仅同一个类能访问js
self.__privateattr 要让内部属性不被外部访问,可把属性名称前加__
继承
class ITBook extends Book {public $technology;public function __construct ($isbn, $title, $author, $technology) {parent:: __construct ($isbn, $title, $author);A对象应用B对象的方法apply (A, arguments);call (A, args1,args2);class ITBook extends Book {constructor (isbn, title, author, technology) {super (isbn, title, author);this .technology = technology;
class Dog(Animal):狗继承动物类,获得动物类的全部功能财产 重载(Overloading) & 重写(Overriding)
php
// 禁用alert alert = function () {}子类的run()覆盖了父类的run(),在代码运行的时候,总是会调用子类的run() 多态同一个接口,使用不同的实例而执行不同操作
php
js
?
C ontrol Flow
if
if 条件1 {执行1 else if 条件2 {执行2 else {执行3 第一种方式同java if (条件1 ):执行1 elseif (条件2 ):执行2 else :执行3 endif ; if (条件1 ){执行1 else if (条件2 ){执行2 else {执行3 if 条件:elif 条件2:else: if [ $1 -gt 30 ];then elif [ $1 -gt 20 ];then else echo 'you are young'fi 注意[ ]两边都得要有空格 if [ ! -n "$1" ]; then # 变量是否存在 if [ ! -d "web-cms" ]; then # 目录是否存在 if [ ! -f "spm.zip" ]; then # 文件是否存在 if [[ "" =~ ^[0-9]{0,2}$ ]]; then # 正则条件双括号[[ ]] 三元运算符
let number = if x > 0 { x } else { -x };
$x > 0 ? $x : -$x
x=(x > 0 ? x :-x)
-
-
switch
-
switch (n) {case 0:echo "no hits";break ;case 1:echo "one hit";break ;default :echo n." hits";switch (n) {case 0:log ("no hits");break ;case 1:log ("one hit");break ;default :log (n+" hits");为什么Python没有switch? if elif func ()case $1 inecho "小少爷"echo "小公主"echo "有没有搞错"esac match
match
match
-
-
-
while 🔁
1┏━▶⚙━━┓
━━▶while◀━━┛
0┗━━━━━▶
a period of time.
while i < 100 { while ( i < 100 ) { while ( i < 100 ) { while i < 100 :while [ $i -lt 10 ]; do done while true; do # 无限循环用Exit跳出 do while 🔁
━━▶⚙◀━━━┓1 0
┗━━while━━▶
和while循环十分类似,至少执行一次 代码
没有do while 用loop loop {if i > 100 {break;
do {while (i<=100);do {while (i<=100);无,用break跳出 for循环 🔁
for item in arr {for (i=1;i<=5;i++) {for (i=1;i<=5;i++) {for i in range (1,6): # range为遍历辅助 for i in `seq 1 3`;do echo $i;done for i in 1 2 3;do echo $i;done break, continue跳出最近一层 的for,for-in,while,do-while循环, 或跳出switch
break , continue break , continue break , continue break , continue break , continue exit
-
exit (); // 别名die, 输出一个消息并且退出当前脚本 -
os._exit () # 终止程序 exit () # 会引发一个异常,如果异常没被捕获,python解析器将会退出,如果被捕获,还可以执行后面的代码,用于做清理工作 exit ()即可,一般在fork出来的子进程中使用os._exit ()
exit Sleep 🚦⏱
use std::thread;use std::time::Duration;sleep (5)const sleep = sec => new Promise (resolve => setTimeout (resolve, sec * 1000));await sleep(5)
import time
sleep 5 异常的抛出与捕获无论异常是否发生,在程序结束前,finally中的语句都会被执行
无try catch用panic!("err info");
//主动抛出异常 function checkNum ($number){if ($number>1){throw new Exception("不能使用大于1的值");return true;try {checkNum (2);catch (Exception $e){echo '错误描述: ' .$e->getMessage ();finally {echo "always excute";//被动抛出异常 try {adddlert ("Welcome!");catch (err){alert (err);//ReferenceError: adddlert is not defined //主动抛出异常 try {throw "抛出错误"catch (err){alert (err);//抛出错误 finally {console.log ("always excute")}# 被动抛出 import systry :open ('myfile.txt')readline ()int (s.strip ())except OSError as err:print ("OS error: {0}".format (err))except ValueError:print ("Could not convert data to an integer.")except :print ("Unexpected error:", sys.exc_info ()[0])finally :print ("always excute")# 主动抛出 try :raise ValueErrorexcept :print ("value error")npm run build || (echo '编译失败';exit 1)if [ $? -ne 0 ];then echo '编译失败'exit 1else echo '编译成功'fi
函数式/管道
let result: String = "Hello"chars ()map (|c| c.to_ascii_uppercase ())collect ();PHP 8.5新增管道,以前仅多层函数嵌套 |> str_split (...)|> (fn($x) => array_map (strtoupper (...), $x));"Hello".split ('').map (item => item.toUpperCase ())
PHP式多层函数嵌套 | CL I 命令行
cargo build 会先安装依赖(如果没有安装),然后编译cargo run --bin hello 编译并运行指定cargo check 检查是否能编译,不会产生执行文件,比build快cargo build --release (生产版)比cargo build(调试版)生成的可执行文件更小运行更快 但不能调试(变量名丢失 断点失效)php -f index.phpphp -r "echo 'mark';"node bgt.js fileTypeScript tsc main.ts // 编译成main.js python3 cmd.py ip 116.6.65.67Method 1: bash backupdb.sh arg1 arg2Method 2: # need shebang and X permission REPL
-
php -anode python3 -
参数
use std::env;fn main () {collect ();println! ("共有{}个参数,第一个参数是{}", args.len () - 1, args[1];$argv 数组
Node.js const args = process .argv.slice (2)process.argv[0] 是node程序地址,process.argv[1] 是脚本名 import sys#需要模块:sys #脚本名:cmd.py #参数1:ip 脚本中$1 的值便是arg1, $2 便是arg2, $@ 值是所有参数arg1 arg2
输入
use std::io::{self, Write};fn main () {print! ("M>> ");stdout ().flush ().unwrap (); // 立即输出提示符 let mut input = String::new ();stdin ().read_line (&mut input).expect ("读取输入失败");println! ("{}", input.trim ());fwrite (STDOUT, "M>>");echo fgets (STDIN);const readline = require ('readline').createInterface ({question ('M>> ', taskid => { // readline.close(); command = input ("M>>")print (command)
read -p "M>> " taskidecho $taskid调用命令行
相对不太好用,代码行多,start命令无法执行,写脚本还是用sh import os-
D isk I/O
判断目录/文件是否存在
use std::fsif fs::metadata("D:\\doc").is_ok() {println! ("目录存在");if fs::metadata("D:\\doc\\1.txt").is_ok() {println! ("文件存在");
if (file_exists ('dirNameOrFileName')) {echo "文件或目录存在";const fs = require ('fs')if (fs.existsSync ('/path/dir')){if (fs.existsSync ('/path/file.txt')){ import osif not os.path.exists (aim_dir+'\\'+name):# 如果文件/目录不存在 isdir (ori_dir+'\\'+name):# 是否是目录 isfile (ori_dir+'\\'+name):# 是否是文件 if [ ! -d "web-cms" ]; then # 目录是否存在 if [ ! -f "spm.zip" ]; then # 文件是否存在
Create/Remove directory/file, write/read file
use std::fs;fn main () -> Result<(), Box> {let mut file = fs::File::create("D:\\doc\\1.txt")?;write ("写入内容".as_byte())?;
mkdir ("/path/to/my/dir", 0700);fopen ("f.txt", "w");fwrite ($f, 'content');fclose ($f);带Sync的函数都是同步方法,没有回调 mkdirSync ('/path/newdir')rmdir ('/path/dir',()=>{console.log('callback')})INSERT: appendFileSync ('./txtdb/db1.tb1.csv', 'Ryan,5\n') // 追加加入 SELECT: readFile ('./txtdb/db1.tb1.csv', (err,data) => {log (data.toString ().split ('\n').filter (item => item)[1].split (',')[0])REPLACE: writeFileSync ('./txtdb/db1.tb1.csv', tb1.map (item => item.join (',')).join ('\n')) // 不存在则新建文件 unlinkSync ('/path/file.txt')// 删除文件 import osmakedirs (aim_dir)open ('f.txt','w') write ('content')writelines (['content\n','content2\n'])close ()mkdir wwwtouch fileecho 'content' >> file
获得文件扩展名
-
const path = require ('path');extname ('/path/file.txt')) // .txt import ossplitext ('a.b.txt') # ('a.b', '.txt') file=a.b.txtecho "${file%.*}" # a.b echo "${file##*.}" # txt
遍历文件
带Sync的函数都是同步方法,没有回调 const fs = require ('fs');const path = require ('path');function traverseDir (dir) {const files = fs.readdirSync (dir); // 读取目录 for (let file of files) {const filepath = path.join(dir, file);const stats = fs.statSync (filepath); // 获取文件信息 if (stats.isDirectory ()) {traverseDir (filepath);else {traverseDir ('/path/dir')import osfor dirpath, dirnames, filenames in os.walk (path):print (dirpath)print (filenames)-
netW ork I/O
HTTP Data
-
$_POST $_GET $_COOKIE判断协议,别忘记考虑负载均衡
window.location, document.cookieconst urlParams = new URLSearchParams (location.hash.replace (/^.*\?/, ''))get ('param')
?
-
HTTP Server
-
-
Node.js python3 -m http.server [port] // 适合HTML页面 Simple Server Demo
HTTP Client
reqwest
cURL
Fetch fetch (url, {then (res => res.json ())then (response => {})catch (err => {})跨域请求默认不会带上cookie,credentials设置为include 则会带上 禁止修改的标头: Referer等 -
curl wget
T ime
Get Time
echo date ("Y-m-d H:i:s");//Output: 2018-05-03 01:06:54 //Other format date (m);date (H);echo time ();//Output: 1525309469 var d=new Date();log (d.toLocaleString ())//Output: 5/2/2018, 2:18:36 PM parse (new Date())/1000//Output: 1525242393 parseInt (Date.now ()/1000) parseInt ((new Date()).valueOf ()/1000)//Output 1525243045 import time;print (time.strftime ("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime ()))#Output: 2018-05-03 10:17:01 print (int (time.time ()))#Output: 1525310230 echo `date`#Output: Wed May 2 13:54:46 2018 echo "[`date +%Y-%m-%d\|%T\|%A`]"#Output: [2018-05-02|14:14:20|Wednesday] echo `date +%s`#Output: 1525242150 Datetime to Timestamp
echo strtotime ("2018-10-06 02:00:00");//Output: 1538791200 Date.parse (new Date("2018-10-06 02:00:00"))/1000
import datetimeimport timeprint (time.mktime (datetime.datetime.strptime ("2021-05-12 02:37:29", "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S").timetuple ()))// output: 1620758249.0 -
Timestamp to Datetime
echo date ("Y-m-d H:i:s",'1538791200000'/1000); // output:2018-10-06 02:00:00 function formatDate (_timestamp) {let date = new Date (+_timestamp),getFullYear (),String (date.getMonth () + 1).padStart (2, '0'),String (date.getDate ()).padStart (2, '0'),String (date.getHours ()).padStart (2, '0'),String (date.getMinutes ()).padStart (2, '0'),String (date.getSeconds ()).padStart (2, '0');return `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hour}:${min}:${sec}`formatDate from datetime import datetimeprint (datetime.fromtimestamp (1620758249))// output: 2021-05-12 02:37:29 -
其他
new Date(new Date(2023,2,0).getTime () + (24 * 3600 - 1) * 1000) // Tue Feb 28 2023 23:59:59 ... 获得月底最后一天的最后一秒 E ncryption
base64
[dependencies]println! ("Base64: {}", BASE64_STANDARD.encode ("mark李"));let decoded_bytes = BASE64_STANDARD.decode ("bWFya+adjg==").expect ("Base64 decode failed");let decoded_str = String::from_utf8(decoded_bytes).expect ("Invalid UTF-8");println! ("Original: {}", decoded_str);
echo base64_encode ("mark李"); // bWFya+adjg== echo base64_decode ("bWFya+adjg=="); // mark李 window.btoa (unescape (encodeURIComponent ("mark李"))); //'bWFya+adjg==' atob ('bWFya+adjg=='))); // 'mark李'
import base64print (base64.b64encode ("mark李".encode ("utf-8")).decode ("utf-8")) // bWFya+adjg== print (base64.b64decode ("bWFya+adjg==").decode ("utf-8")) // mark李 echo -n mark李|base64 // bWFya+adjg== 加-n 来确保字符串不包含行末换行符 echo bWFya+adjg==|base64 -d // mark李% echo mark李|base64 // bWFya+adjgo= echo bWFya+adjgo=|base64 -d // mark李
Hash: md5, sha1, sha256, sha512保存密码的算法: sha256(pwd+salt)
[dependencies]let digest = md5::compute("mark李");println! ("{:x}", digest);
echo md5 ("mark李"); // 8ef85f394180bc4a79a47b033440d7fd md5 calculate(.trans.) md5 ("mark李"); // 8ef85f394180bc4a79a47b033440d7fd import hashlibmd5 (bytes ('mark李',encoding='utf-8')).hexdigest ()) // 8ef85f394180bc4a79a47b033440d7fd import ossha1 (open ('C:\\Users\\m\\Desktop\\file.exe','rb').read ()).hexdigest ()sha256 (...sha512 (...echo -n mark李|md5sum # 8ef85f394180bc4a79a47b033440d7fd - echo -n mark李|openssl md5 # 8ef85f394180bc4a79a47b033440d7fd cat file|md5sum cat file|openssl sha1 cat file|openssl sha256 cat file|openssl sha512
对称加密: AES推荐使用AES GCM模式(高效且安全) 禁止使用易被暴破的DES/RC2.
[dependencies]
$iv='';openssl_decrypt (hex2bin ($key), "aes-128-ecb", $aeskey, OPENSSL_RAW_DATA, $iv);openssl_encrypt
在线AES加解密工具 ?
?
非对称加密: RSA链路加密采用TLS1.3及以下,禁止使用TLS1.1及以下。Devtools Security选项卡可看版本
[dependencies]
?
Web Crypto API
?
ssh-keygen -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/markli_rsa -N ""read -p "输入目标IP>> " ipscp ~/.ssh/markli_rsa.pub root@$ip:~/markli_rsa.pubssh root@$ip "cat ~/markli_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"ssh root@$ip "rm ~/markli_rsa.pub"